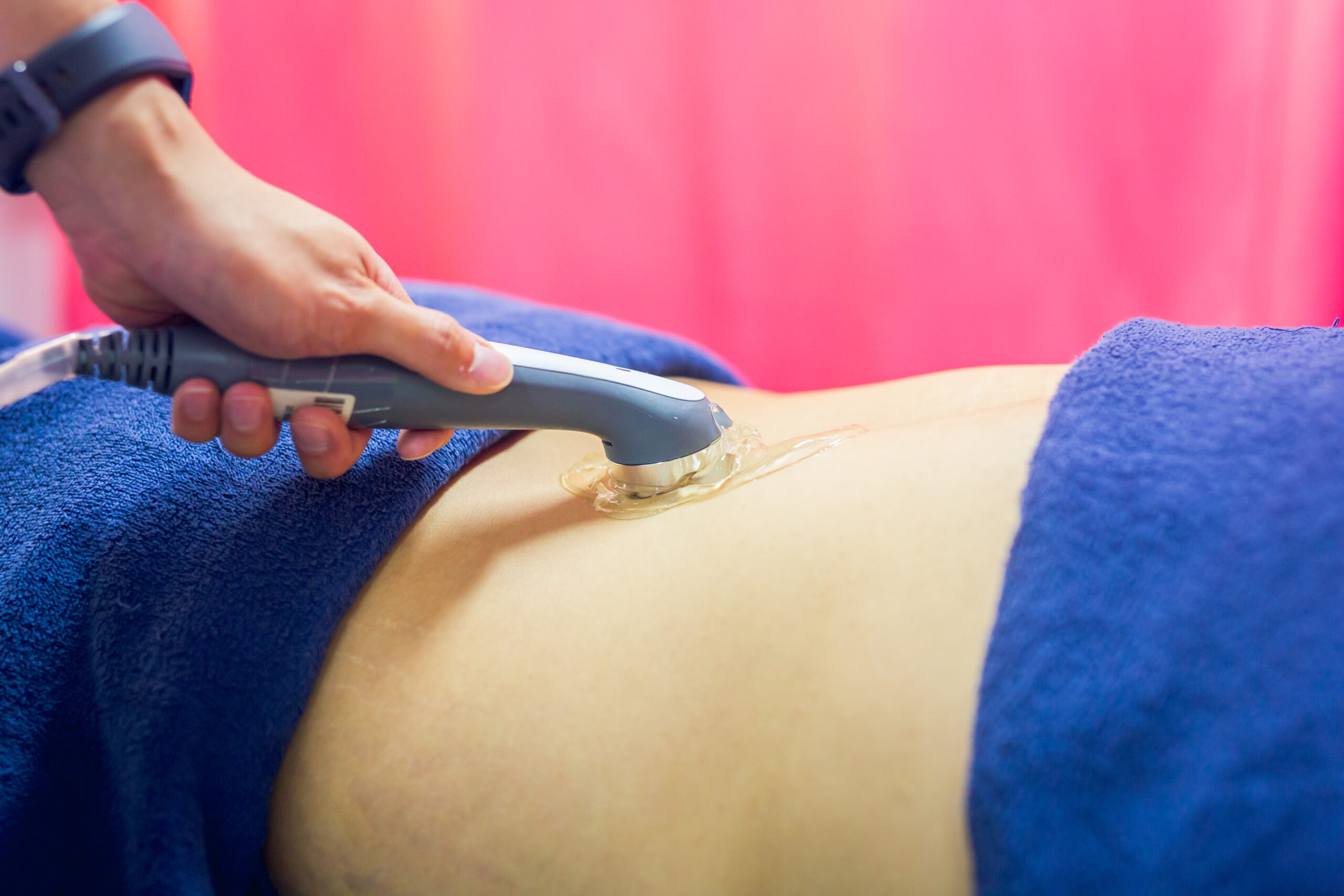
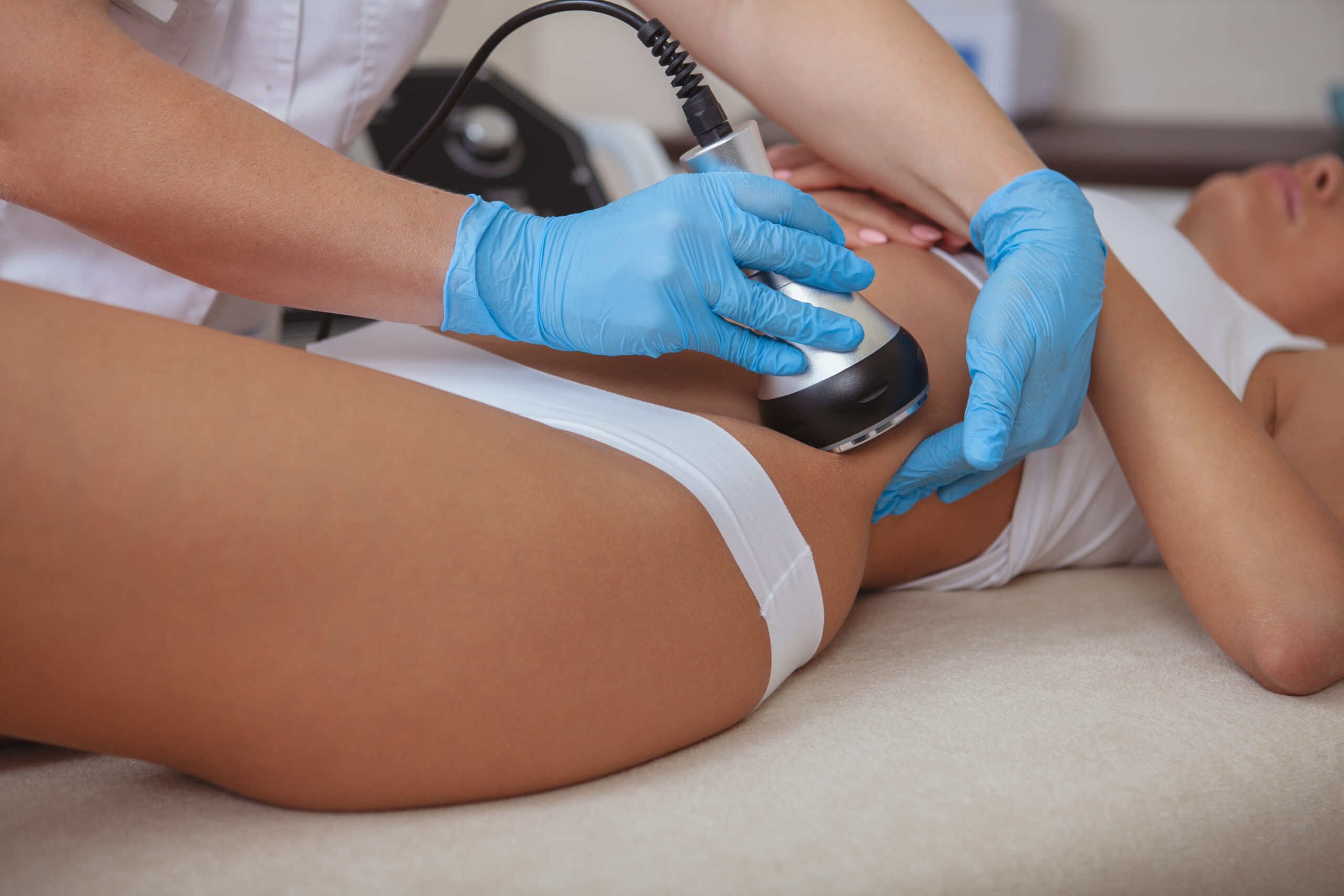

Ultrasonic cavitation is a non-invasive procedure that uses ultrasonic waves to reduce localized fat deposits in the body. It works by producing low-frequency sound waves that create tiny bubbles or cavities within the fat cells. As these bubbles collapse, they cause the fat cells to break down and release their contents, which can then be eliminated from the body through natural processes.
The treatment typically involves the use of a handheld device that is placed on the skin in the area being targeted. The device emits low-frequency sound waves that penetrate the skin and create vibrations within the fat cells. These vibrations cause the fat cells to break apart and release their contents.
Ultrasonic cavitation is often marketed as a way to lose weight and reduce body fat. However, it is important to note that while the procedure can be effective in reducing localized fat deposits, it is not a weight loss solution and is not recommended as a replacement for a healthy diet and exercise regimen. Additionally, the results of ultrasonic cavitation treatments can vary depending on a variety of factors, including the individual’s body composition, lifestyle habits, and the specific treatment protocol used.
The frequency of ultrasonic cavitation used in the procedure for weight loss typically ranges between 20 to 70 kHz. Most handheld devices are in the 40kHz range.
However, the exact frequency used may vary depending on the device and the specific treatment protocol. The frequency is chosen based on the depth of the fat deposits being targeted and the specific area of the body being treated. Lower frequencies are typically used for targeting deeper fat deposits, while higher frequencies may be used for more superficial fat deposits. The frequency of ultrasonic cavitation used in the procedure is important because it determines the depth of penetration and the intensity of the treatment.
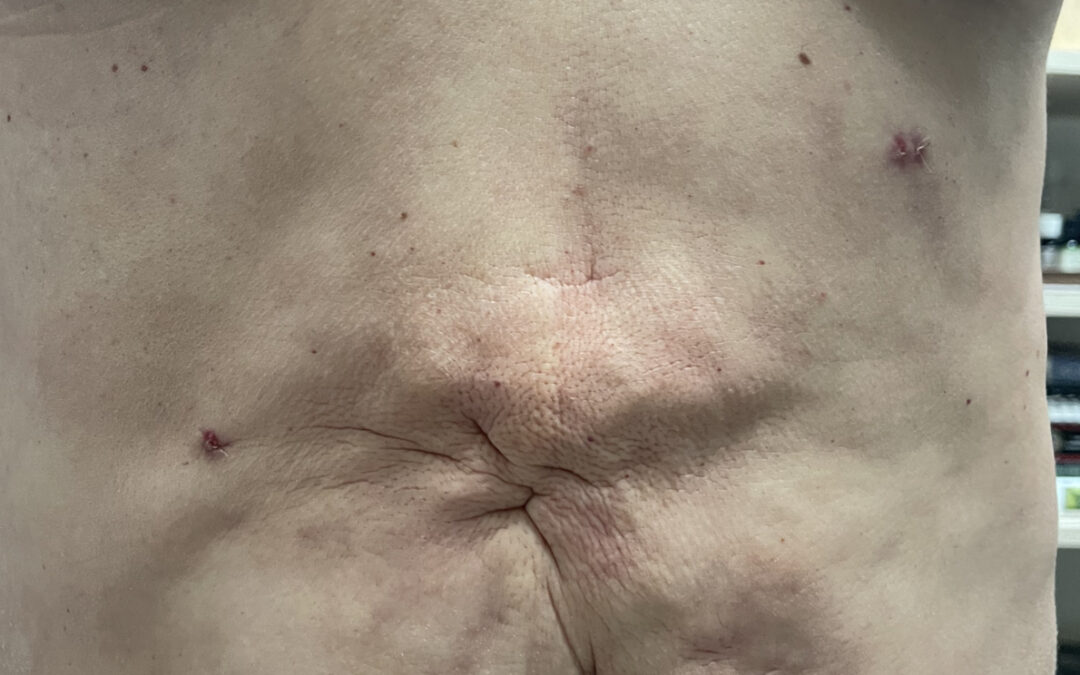
There is some controversy and debate in the medical community about whether ultrasonic cavitation can cause liposuction fibrosis. Liposuction fibrosis is a condition that can occur after liposuction surgery, where scar tissue develops around the treated area, leading to a lumpy or uneven appearance.
Some studies have suggested that ultrasonic cavitation can cause liposuction fibrosis by damaging the connective tissue in the treated area, which can lead to scarring and a lumpy appearance.
Additionally, the risk of liposuction fibrosis may be reduced by using proper technique and appropriate treatment protocols, e.g., following doctor’s orders, appropriate compression garments with foam, staying hydrated, and starting manual lymphatic drainage as soon as possible.
If you are considering ultrasonic cavitation for weight loss, it is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits with a qualified healthcare professional, who can help you make an informed decision about whether the procedure is right for you.
Therapeutic ultrasound is a form of “electrophysical” therapy modality that uses high-frequency sound waves (1 – 3 Mhz range) to promote healing and reduce pain. It is commonly used in post-operative care to help speed up the healing process and reduce inflammation.
After surgery, scar tissue can form around the surgical site, which can limit mobility and cause discomfort. Therapeutic ultrasound, including the combination with manual lymphatic drainage, can be used to break up this scar tissue and promote the growth of healthy tissue, which can help to reduce pain and improve range of motion.
Therapeutic ultrasound can also increase blood flow to the affected area, which can bring important nutrients and oxygen to the tissue, helping it to heal more quickly. Additionally, ultrasound can help to reduce inflammation by promoting the release of cytokines, which are molecules that help to regulate the immune response.
The specific treatment parameters for therapeutic ultrasound will depend on the individual’s condition and the stage of healing post-surgery. The therapist may adjust the frequency, intensity, and duration of the ultrasound to optimize the therapeutic effect.
It’s worth noting that therapeutic ultrasound should only be performed by a licensed healthcare professional with training in the technique. It should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment and should only be used as part of a comprehensive post-operative rehabilitation program.
Therapeutic ultrasound has been shown to assist in both angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, which are processes that involve the formation of new blood vessels and lymphatic vessels, respectively.
Angiogenesis is important in the healing process as it promotes the growth of new blood vessels, which can bring nutrients and oxygen to the affected tissue. Therapeutic ultrasound has been shown to increase the expression of growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which can stimulate angiogenesis.
Lymphangiogenesis involves the formation of new lymphatic vessels, which play a key role in immune function and the removal of excess fluid and waste products from tissues. Therapeutic ultrasound has also been shown to stimulate the expression of lymphangiogenic growth factors, such as VEGF-C and VEGF-D, which can promote lymphangiogenesis.
By promoting both angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, therapeutic ultrasound can help to accelerate the healing process and improve the overall function of the affected tissue. However, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms involved and to determine the optimal treatment parameters for promoting these processes using therapeutic ultrasound.
Therapeutic ultrasound can also be helpful in the treatment of liposuction fibrosis. Liposuction fibrosis refers to the development of fibrous scar tissue and firm lumps or bumps that can occur after liposuction. This condition can be uncomfortable and may lead to a loss of symmetry in the treated area.
Therapeutic ultrasound can be used to break up the fibrous tissue and improve the overall appearance and texture of the skin in the treated area. The ultrasound waves penetrate the skin and can reach deep tissue layers, helping to break up scar tissue and promote the growth of healthy tissue.
By promoting circulation and tissue regeneration, therapeutic ultrasound can help to reduce the appearance of fibrosis and improve overall skin health.
It’s important to note that the treatment parameters for therapeutic ultrasound will vary depending on the individual’s condition and the severity of the fibrosis. A trained healthcare professional should assess the patient and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Using therapeutic ultrasound incorrectly, particularly by an untrained professional, can potentially lead to several dangers and complications. Some of these include:
1) Burns: If the ultrasound probe is left in one spot for too long or the intensity of the ultrasound is too high, it can cause burns on the skin, surgical site, and even deep into the outside bone tissue;
2) Tissue damage: If the ultrasound is applied to a sensitive area such as a joint, it can cause tissue damage;
3) Increased pain: If the ultrasound is applied incorrectly or at an inappropriate frequency, it can increase pain and discomfort rather than reduce it;
4) Nerve damage: If the ultrasound is applied too close to a nerve, it can cause nerve damage and lead to a loss of sensation or other neurological symptoms;
5) Fetal damage: If the ultrasound is used on a pregnant woman, it can potentially harm the developing fetus, particularly during the first trimester; &
6) Masking underlying conditions: Therapeutic ultrasound may provide temporary relief from pain or discomfort, but it may mask underlying conditions that require medical attention.
It is important to note that therapeutic ultrasound should only be administered by a licensed healthcare professional who has received appropriate training and has experience in using the technique. Patients should also communicate any discomfort or pain they experience during the treatment to the therapist. If used correctly, therapeutic ultrasound can be a safe and effective treatment for a variety of conditions.